Merge Sort
merge sort를 이용하여 inversion 개수세기
[1517 버블 소트] https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1517 .
inversion의 개수를 센다.
문제상황 파악하기.
버블소트는 arr[i]>arr[i+1]이면 swap하면서 진행하는 정렬 방법이다.
그리고 이는 당연하게도 O(n^2)이 걸린다.
그리고 당연하게도 그대로 구현하면 시간초과다 그러면 실버급이겠지.
O(NlogN)까지는 허용 될 것이므로 다른 방법을 찾아야한다.
inversion?
i < j 일 때 arr[i] > arr[i+1] 일때 (arr[i], arr[i+1])의 쌍을 inversion이라고 한다.
결국 이 문제는 모든 inversion의 개수를 세는 것이다.
inversion을 세는 방법은 merge sort, bit, segment tree 등 여러가지가 있지만 merge sort를 이용해 구해보자!
[참고자료] https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/counting-inversions-in-an-array-using-segment-tree/?ref=gcse
나는 위의 링크를 참고 했다.
아이디어 얻기.
merge sort는 Divide & Conquer를 이용한다.
분해되고 병합되는 과정은 아래 그림과 같다.
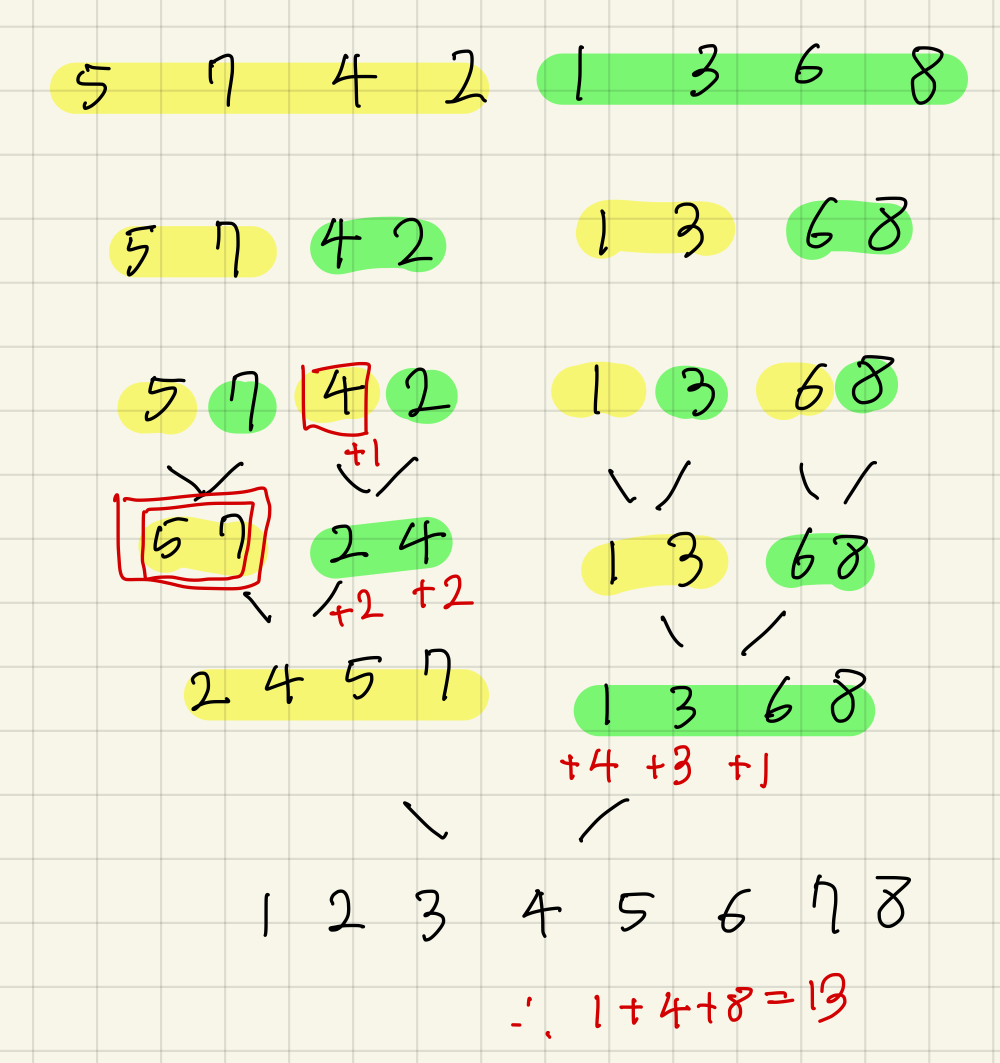
최대한 절반으로 나눠서 효율적인 계산을 하도록 하고,
노란색, 초록색으로 분해 되고 병합된다. 그 과정에서 빨간색 박스로 inversion을 센다.
병합하는 과정에서 mid-i개(앞인데 더 큰거의 개수)를 계속 더해주는 것이다.
주의할 점
값이 long long을 넘어갈 수 있다. 범위를 보면 쉽게 알 수 있다.
(근데 난 한번 틀렸다 제출하자마자 아차 했다 ㅋㅋ)
실제 코드
나머지 주의 할 점은 코드에 주석으로 처리했다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#define fast_io cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL); ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int n;
ll arr[500001];
ll merge(ll arr[], ll temp[], int left, int mid, int right){
int i, j, k;
ll inv_count = 0;
i = left; j = mid; k = left;
while (i<mid&&j<=right){
if(arr[i]<=arr[j]){
temp[k++] = arr[i++];
}else{
temp[k++] = arr[j++];
//mid는 right덩어리의 처음 index이다.
inv_count += mid-i;
}
}
//남은거 다 넣어
while (i<mid) temp[k++] = arr[i++];
while (j<=right) temp[k++] = arr[j++];
//원래 배열로 다 옮겨
for(i= left;i<=right;i++) arr[i] = temp[i];
return inv_count;
}
ll _mergeSort(ll arr[], ll temp[], int left, int right){
int mid; ll inv_count=0;
if(right>left){
mid = (left+right)>>1;
inv_count += _mergeSort(arr, temp, left, mid);
inv_count += _mergeSort(arr, temp, mid+1, right);
inv_count += merge(arr, temp, left, mid+1, right);
}
return inv_count;
}
ll mergeSort(ll arr[], int array_size){
ll temp[array_size];
return _mergeSort(arr, temp, 0, array_size-1); //mergesort call-by-address
}
int main(){
fast_io;
cin >> n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cin >> arr[i];
cout << mergeSort(arr, n);
}